Networks - CNOP - WiFi 1
-
Wireless equivalent of the copper example
-
Access points connects stations to aggregation layer
-
Many APs multiplex larger wireless networks, e.g. a campus
Description
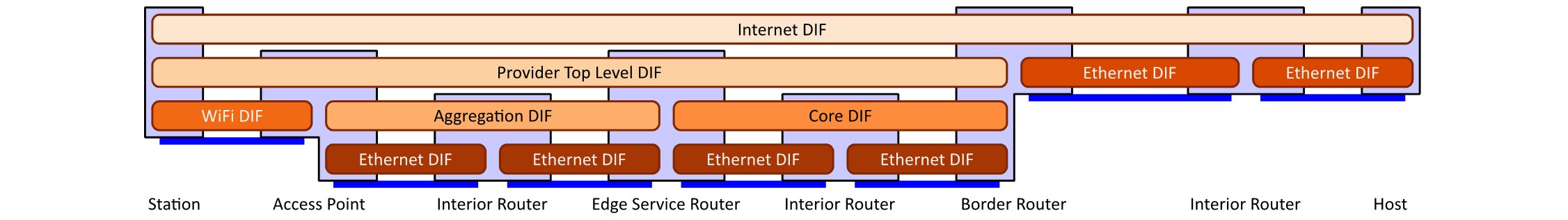
This is the wireless equivalent of the fixed access network Copper. It shows a WIFI network were an AP — an access router — provides wireless access to a group of stations (STA). The traffic of AP is multiplexed over the aggregation networks into one or more edge service routers, which forward traffic to other edge service routers via the core network or to border routers if the destination is outside of the provider’s network.
The chosen DIF structure is as follows: WiFi manages IPC over a wireless link between APs and stations. Provider Top Level aggregate traffic from multiple APs into the edge service router(s). It works on top of Aggregation in the segment between the AP and the edge service router(s). It works on top of Core in the segment between the edge service router(s) and the border router(s). It handles mobility of hosts (stations) within the service provider network, realising seamless roaming.
Schema

3D